Managing an on-premises data center can be challenging. Configuring the network and firewall, installing the operating system, putting virtualization into practice, buying and installing hardware, and configuring storage are just a few of the many things that need to be done. And once it’s all up and running, you’re responsible for maintaining it throughout its entire lifecycle. But there’s a simpler way: Cloud computing.
You don’t have to worry about maintenance because when you go with the cloud, the vendor takes care of the hardware for you. Additionally, you can hire a variety of software and platform services from them as needed. The best part? You just pay for the actual services rendered.
The cloud gives you an easy-to-use online portal where you can quickly manage your computing, storage, network, and application resources. Convenient, and adaptable, and it spares you the hassle of handling things on your own.
Gartner predicts that cloud computing will become a business necessity by 2028, transforming the way organizations operate and compete.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing lets you store and access your data and programs on remote servers via the internet instead of relying on your computer’s hard drive or a local server. Think of it as internet-based computing, where you get the resources you need as a service through the web. This means you can store everything from files and images to documents online.
Cloud computing allows you to control your data and apps from any location and so it is an effective tool for both personal and professional use.
With cloud computing, you can do the following:
- Store, back up, and recover your data effortlessly
- Access software whenever you need it, on-demand
- Develop new applications and services with ease
- Stream videos and audio seamlessly
Want to learn more about Cloud computing? Enrol in our Salesforce Administrator course!
Brief History and Evolution of Cloud Computing
Today, cloud computing is everywhere. The foundation for cloud computing was established by the internet boom of the 1990s, building on the work of Mainframe computing in the 1950s. The term “cloud computing” gained traction when companies like Amazon, Google, and Salesforce started offering web-based services in the early 2000s. Because of this idea, computing resources might be accessed via the internet, providing scalability, flexibility, and financial savings.
This shift has led to significant growth in the cloud market, with the U.S. market size reaching USD 97.44 billion in 2022 and projected to grow to USD 458.45 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 16.80%.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Cloud computing lets you easily access computing resources like storage and processing power over the internet, instead of relying on local hardware. Here’s a brief explanation of how it works:
- Infrastructure: Cloud computing relies on remote servers hosted online to store, manage, and process data.
- On-Demand Access: You can access cloud services whenever you need them, scaling up or down without investing in physical hardware.
- Service Types: Cloud computing offers cost savings, scalability, reliability, and accessibility, reducing capital expenses and boosting efficiency.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
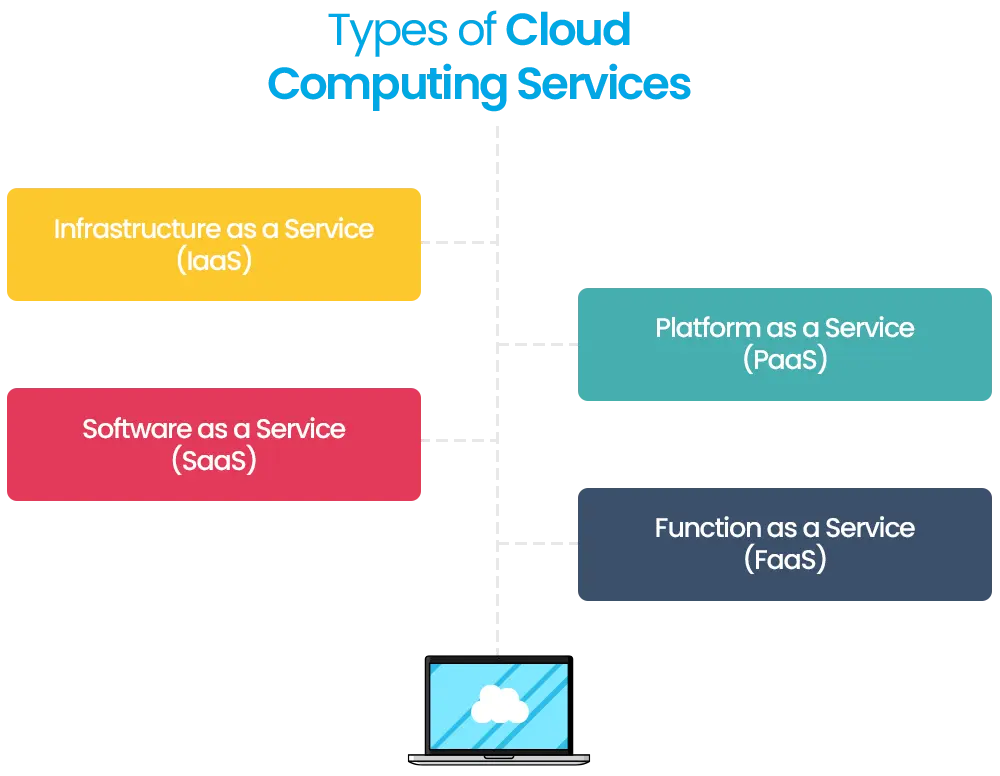
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
With IaaS, you can rent IT infrastructure like servers, virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networks from a cloud provider. For example, you can set up a VM running Windows or Linux and install whatever you need on it. IaaS gives you maximum flexibility but requires you to handle most of the maintenance.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers an on-demand environment for developing, testing, and managing software applications. While you focus on building your app, the cloud provider manages the underlying environment. PaaS is less flexible than IaaS, but it takes the burden of managing the infrastructure off your shoulders.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS uses the internet to deliver software, usually on a subscription basis. Microsoft OneDrive, Dropbox, and Office 365 are a few examples. SaaS reduces operating costs by providing software that is centrally hosted and controlled.
Function as a Service (FaaS)
FaaS, also known as serverless computing, allows you to run code in response to events without worrying about server maintenance. It operates on a “pay as you go” model, scaling automatically with your workload, which promotes agility in development and deployment.
Cloud Deployment Models

1. Public Cloud
The public cloud is all about flexibility and accessibility. Its pay-as-you-go business model makes it simple to scale up or down as necessary. This strategy is economical since it offers the services that companies require without requiring a big initial outlay.
This strategy is highly economical, as evidenced by the projected growth in public cloud spending, which is forecast to reach $675.4 billion in 2024, representing a 20.4% increase from the previous year.
2. Private Cloud
The private cloud is the best option for companies with specific security and compliance needs. It provides enhanced security and the flexibility to adapt cloud resources to particular needs. It’s perfect for businesses that prioritize control over their data and operations.
3. Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud blends the best of both worlds—private and public clouds. It allows seamless data and application processing across environments. This model is ideal for businesses that need to keep sensitive data secure in a private cloud while taking advantage of the scalability of the public cloud for less critical tasks.
4. Community Cloud
The community cloud is designed for collaborative groups, such as government agencies or academic institutions, who share common goals and projects. To ensure that resources are shared safely amongst reliable partners, access is usually limited to community members.
Advantages of Cloud Computing

Cost: With cloud computing you can save big on upfront costs because it avoids expensive hardware and software purchases.
Speed: Even you can get the resources you need in minutes, often with just a few clicks.
Scalability: Easily adjust your resource needs to match your business requirements.
Productivity: With the use of cloud computing you can eliminate operational hassles. With this, you won’t need to worry about patching, hardware maintenance, or software management.
Reliability: You can keep your business running smoothly with quick and cost-effective backup and recovery options.
Security: Many cloud providers offer strong security measures, including advanced policies, technologies, and controls to keep your data safe.
Case Study (How Netflix successfully leveraged cloud computing)
Netflix, a global streaming giant, has heavily relied on cloud infrastructure to scale its operations and deliver high-quality content to millions of subscribers worldwide. By utilizing cloud-based services, Netflix has been able to efficiently manage peak traffic, optimize content delivery, and innovate rapidly.
Challenges and Disadvantages
Security Concerns
Cyberattacks may become more likely if sensitive data is stored on the cloud. There could be a greater chance of data breaches and illegal access to your information, which could have detrimental effects on your company.
Downtime and Reliability
Unexpected outages can occur even with reliable cloud services due to scheduled maintenance, network outages, or server malfunctions. These disruptions have the potential to cause havoc with your company’s operations and annoy clients who rely on your services continuously.
Dependency on Internet Connectivity
Using cloud services requires a stable and fast Internet connection. In areas with poor connectivity, accessing and working with cloud resources becomes challenging, which can hinder productivity and efficiency.
Cost Management Complexity
The pay-as-you-go model of cloud computing seems straightforward but managing and controlling costs can be complicated. Without careful monitoring and optimization, you may encounter unexpected expenses that strain your budget.
Trends on the Rise and Cloud Computing's Future
Major cloud service providers like Google, Microsoft, IBM, and Amazon are driving new trends to offer more cost-effective and efficient services. The leading trends in cloud computing are listed below:
- Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
- Enhanced Data Security
- Multi and Hybrid Cloud Deployments
- Low-Code and No-Code Cloud Solutions
- Edge Computing
- Internet of Things (IoT)
- Kubernetes and Docker
- Serverless Architecture/Computing
- DevSecOps
- Disaster Recovery and Backup
Cloud Computing vs. Traditional IT Infrastructure
|
Aspect |
Cloud Computing |
Traditional Computing |
|
Definition |
Delivers various services like data and programs over the internet using remote servers. |
Provides services using local servers and physical hardware. |
|
Infrastructure Location |
Runs on third-party servers hosted by external providers. |
Operates on physical hard drives and on-site servers. |
|
Data Accessibility |
Gives consumers access to data at any time, from any location, provided they have an internet connection. |
Data can only be accessed on the system where it’s stored. |
|
Cost Effectiveness |
More cost-effective because server costs are shared among multiple users, reducing overall expenses. |
Less cost-effective, as it requires purchasing and maintaining expensive equipment. |
|
User-Friendliness |
More user-friendly, providing internet-based data access from any location. |
Less user-friendly since external storage or transfer is needed to access data from another system. |
|
Internet Dependency |
Relies on a fast, stable internet connection to access data. |
Does not require an internet connection to access stored data. |
|
Storage and Computing Power |
Provides greater storage and computing power, enabling faster and more efficient application performance. |
Offers less storage and computing power compared to cloud solutions. |
|
Scalability and Elasticity |
Offers simple scalability, enabling businesses to modify server and storage capacity based on their needs. |
Requires physical changes in order to expand since it lacks elasticity and scalability. |
|
Maintenance and Support |
The maintenance and support are handled by the service provider. |
Requires an in-house team to manage and maintain systems, which can be time-consuming and costly. |
|
Software Delivery Model |
Software is delivered as a service (SaaS), accessible via subscription, and regularly updated. |
Software must be purchased and installed on each user’s device, with manual updates required. |
Use Cases of Cloud Computing
>> Scalable Infrastructure
Without having to make real hardware investments, enterprises can grow their computing capabilities on demand with Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
>> Efficient Application Development
Platform as a Service (PaaS) simplifies app development, providing tools and environments to build, deploy, and manage applications easily.
>> Streamlined Software Access
Software as a Service (SaaS) offers subscription-based access to software online, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance.
>> Data Analytics
Cloud-based platforms support big data analytics, helping organizations efficiently process and extract insights from large datasets.
>> Disaster Recovery
Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions offer cost-effective data backup and replication, ensuring quick recovery in the event of a system failure.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has eliminated the use of costly on-premise infrastructure which provides scalable, on-demand computing resources. For contemporary businesses, it’s a smart move because it speeds up time to market, improves collaboration, and simplifies resource management.
As technology advances and fundamentally changes the face of IT and company operations, we may expect to see even more cutting-edge cloud-based solutions emerge. By studying cloud computing’s foundations and exploring its numerous applications, businesses may benefit from the potential it offers to foster growth, productivity, and success in the digital age.
The future of business is in the cloud. It is the path to innovation and growth!











